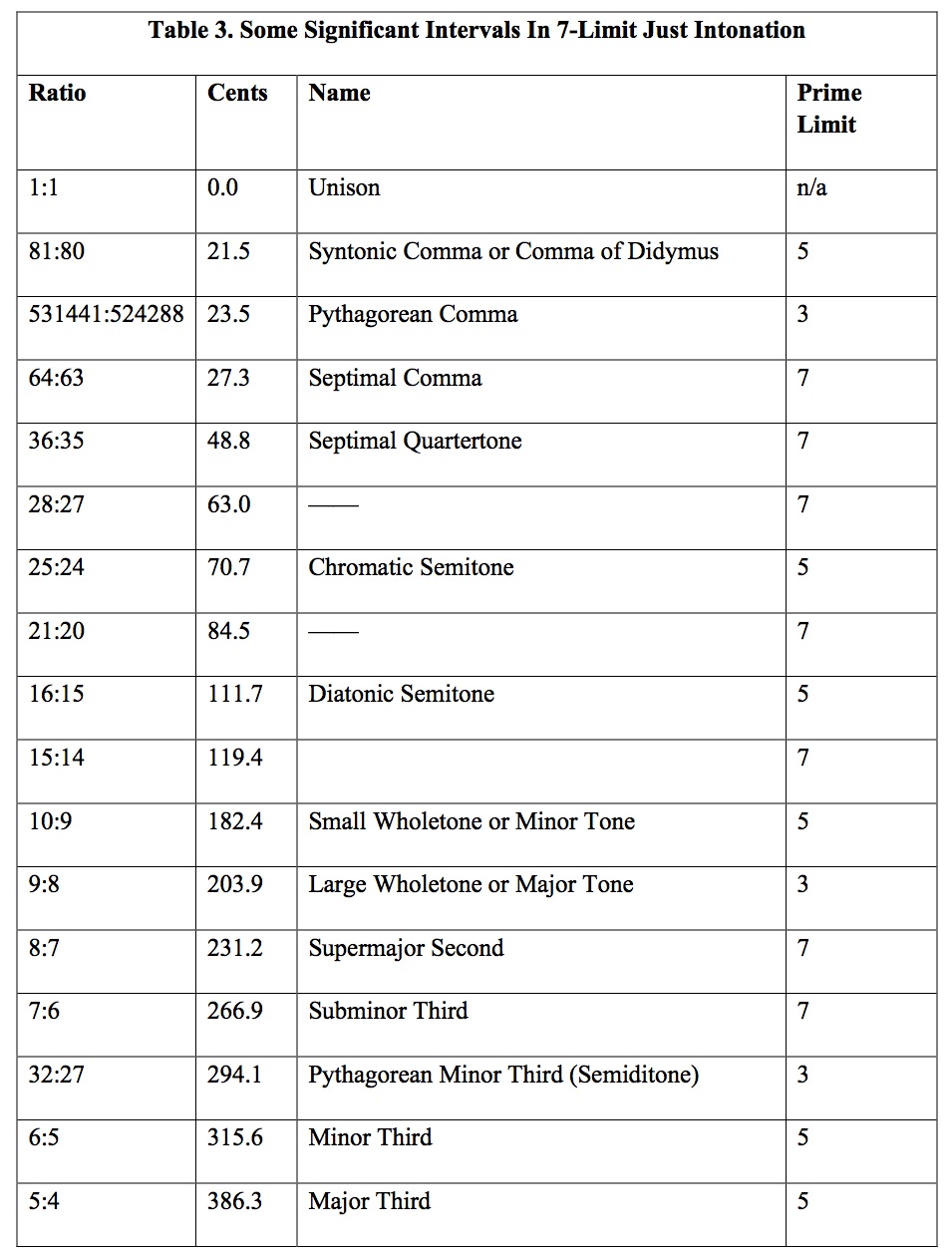
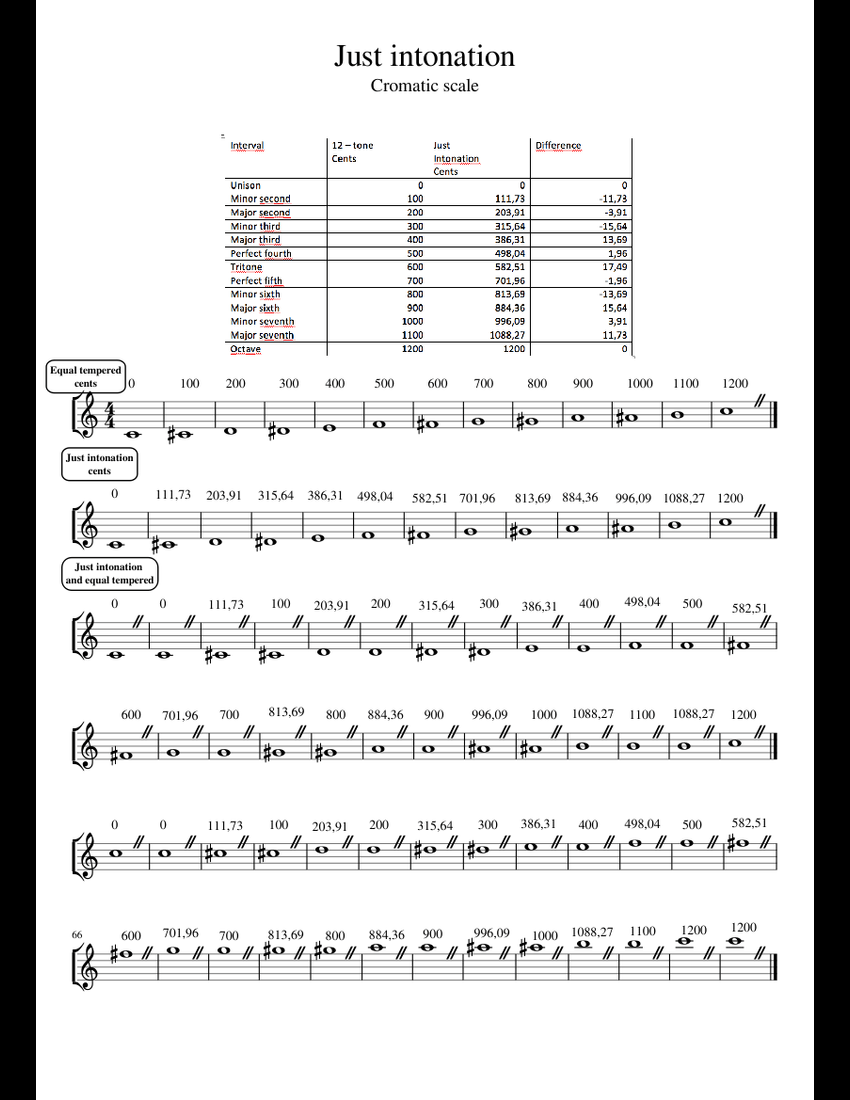
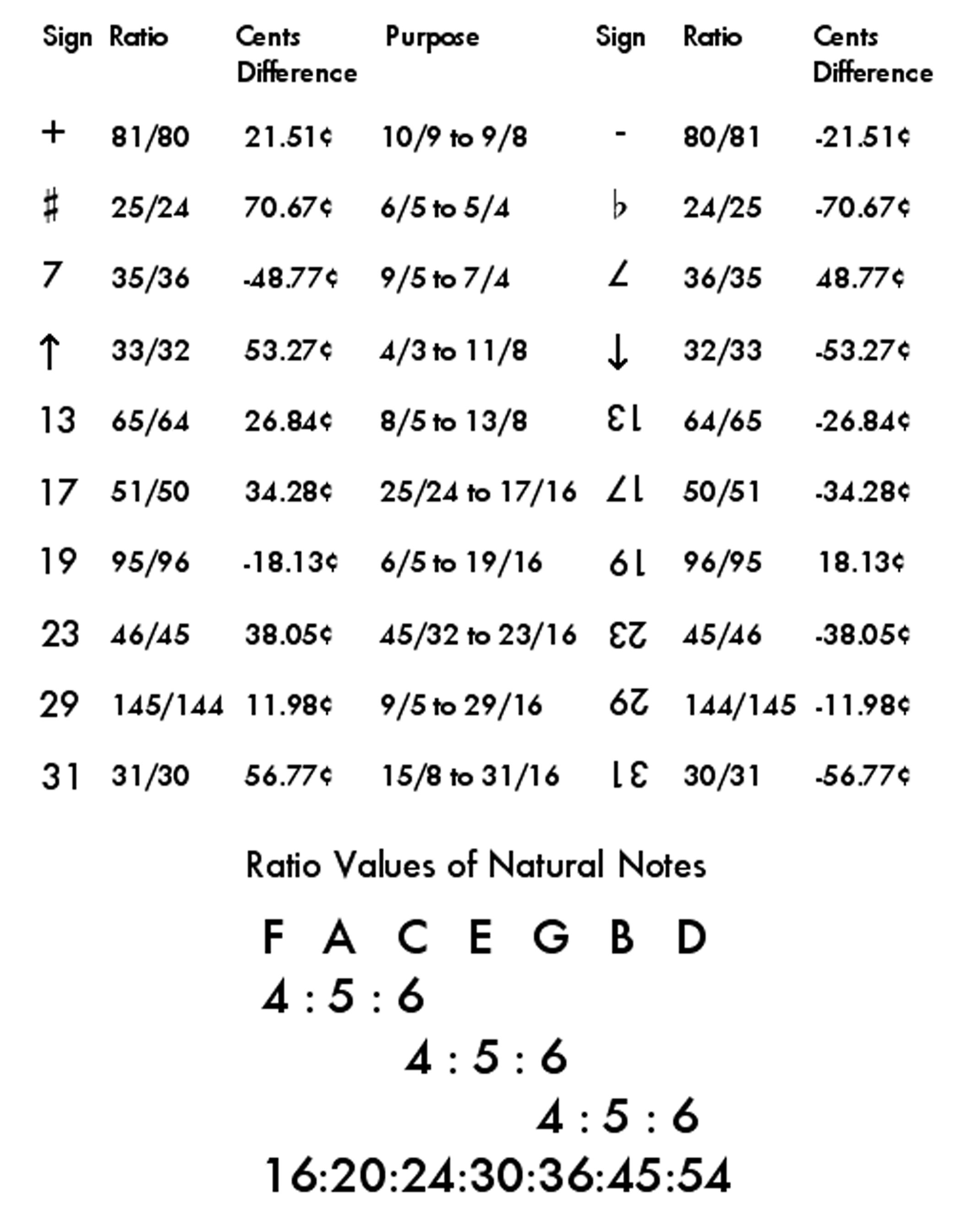
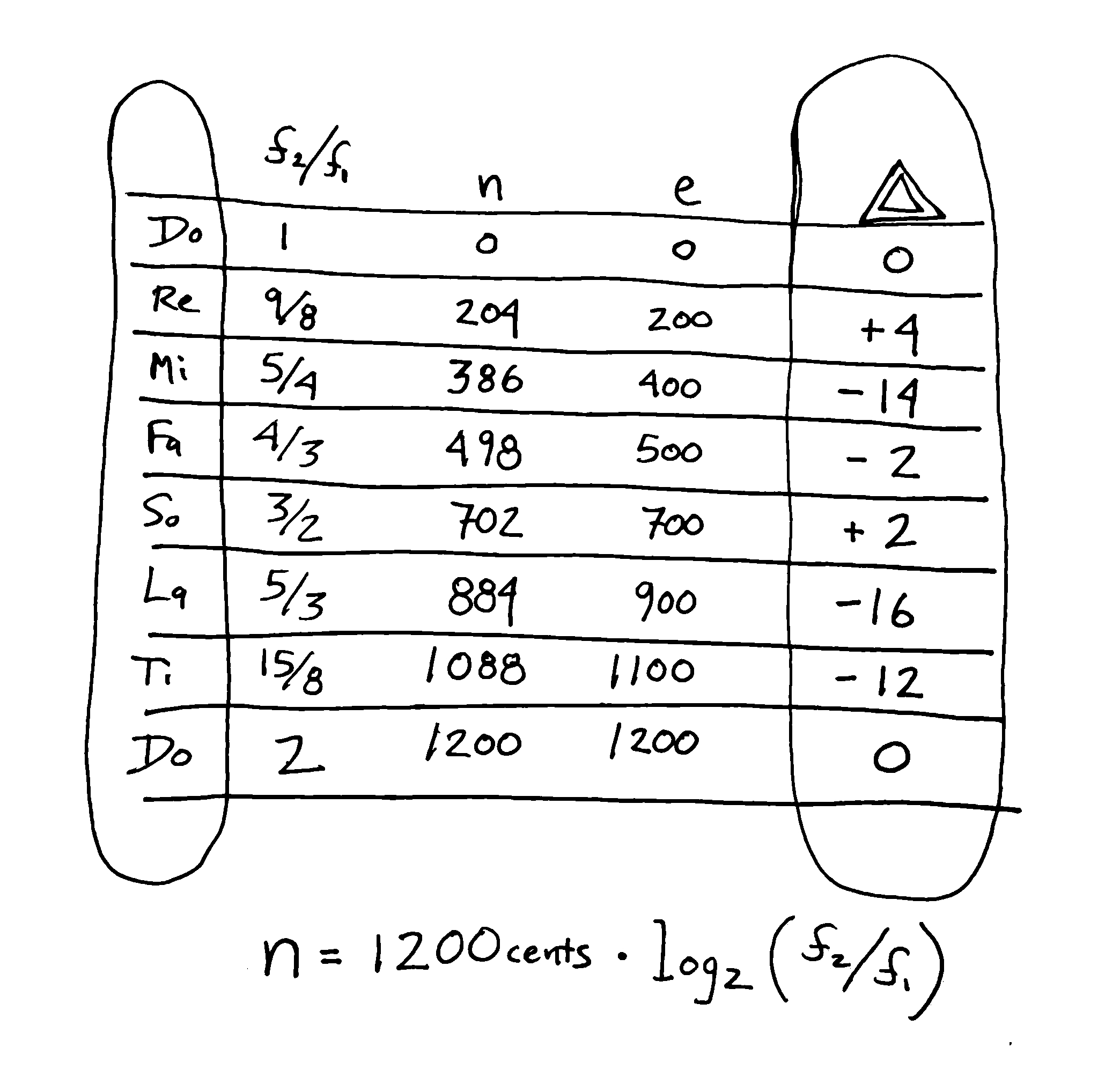
Just Intonation Chart
Just Intonation Chart - Other keys are not, because of math(tm). Web chords of just intonation. Web the following chart shows the various intervals produced between pairs of notes in either scale, as expressed in ratios and cents. Web chords of just intonation all chords are based on root c which is 0 pitch. Half an octave, three whole tones, two minor thirds, etc. The chart below shows how to adjust each pitch of any chord represented on the chart in order to play in tune in a just intonation scheme. The overtones arrange themselves in a series of pure. The 2:1 octave and the 3:2 perfect fifth. All chords are based on root c which is 0 pitch. Know alternate fingerings for specific intonation issues on each instrument. Other keys are not, because of math(tm). The overtones arrange themselves in a series of pure. Web on a piano in just intonation, moving from one tonic to another changes the whole interval makeup of the key, and you get a really specific, visceral feel for where you are on the pitch map. Good tuning notes ch, this is good or) flute oboe bassoon clarinet or saxophone young player older player trumpet Intonation , pythagorean scale, tempered tuning. Web the just intonation primer will give you the information you need, in a succinct and readable form. The chart below shows how to adjust each pitch of any chord represented on the chart in order to play in tune in a just intonation scheme. Et interval lists the size of a given equally tempered (et) interval in semitones from the lower pitch to the upper pitch. Lower and upper partial shows which partials of a harmonic series to which we might choose to tune the et interval to achieve just intonation. Web just intonation (hereinafter “ji”) is any system of tuning in which all of the intervals can be represented by ratios of whole numbers, with a strongly implied preference for the smallest numbers compatible with a given musical purpose. With 84 pages of text and over 50 charts and diagrams, the just intonation primer explains the essential concepts of just intonation in terms that practicing composers and musicians will understand. Web in music, just intonation or pure intonation is the tuning of musical intervals as whole number ratios (such as 3:2 or 4:3) of frequencies. The 2:1 octave and. The first n harmonics account. Other keys are not, because of math(tm). Web the just intonation primer will give you the information you need, in a succinct and readable form. The 2:1 octave and the 3:2 perfect fifth. Lower and upper partial shows which partials of a harmonic series to which we might choose to tune the et interval to. With 84 pages of text and over 50 charts and diagrams, the just intonation primer explains the essential concepts of just intonation in terms that practicing composers and musicians will understand. Below is a chart that shows you what the correct adjustment is for each pitch of the chromatic scale to make it sound in tune (or match) with the. Half an octave, three whole tones, two minor thirds, etc. An interval tuned in this way is said to be pure, and is called a just interval. A tritone has different frequencies depending on definition: Web johnston's notation for just intonation is based on and extends this principle, that every accidental multiplies a pitch's frequency by some defined constant. For. Web just intonation (hereinafter “ji”) is any system of tuning in which all of the intervals can be represented by ratios of whole numbers, with a strongly implied preference for the smallest numbers compatible with a given musical purpose. Web because the basic pitch ratios are 3/2 and 5/4, all pitch ratios are composed of the prime numbers 2, 3. Web because the basic pitch ratios are 3/2 and 5/4, all pitch ratios are composed of the prime numbers 2, 3 and 5. Web just intonation is an intonation scheme in which notes are arranged in fractions of these overtones. Et interval lists the size of a given equally tempered (et) interval in semitones from the lower pitch to the. Web chords of just intonation all chords are based on root c which is 0 pitch. Each musical tone consists of a fundamental resonance and a series of overtones. Web the following chart shows the various intervals produced between pairs of notes in either scale, as expressed in ratios and cents. The chart below shows how to adjust each pitch. Web johnston's notation for just intonation is based on and extends this principle, that every accidental multiplies a pitch's frequency by some defined constant. Web just intonation (hereinafter “ji”) is any system of tuning in which all of the intervals can be represented by ratios of whole numbers, with a strongly implied preference for the smallest numbers compatible with a. Web just intonation is an intonation scheme in which notes are arranged in fractions of these overtones. In this form of just intonation, the highest prime number is. Similarly the perfect fifth is the ratio between the second overtone and the first overtone (i.e. Consequently, the numerator and denominator of each ratio are always a power of 2 or 3.. Web on a piano in just intonation, moving from one tonic to another changes the whole interval makeup of the key, and you get a really specific, visceral feel for where you are on the pitch map. All chords are based on root c which is 0 pitch. Consequently, the numerator and denominator of each ratio are always a power. Web the following chart shows the various intervals produced between pairs of notes in either scale, as expressed in ratios and cents. Web the chart below shows us how to justly tune various common intervals. The first n harmonics account. Web the just intonation primer will give you the information you need, in a succinct and readable form. Intonation , pythagorean scale, tempered tuning. The 2:1 octave and the 3:2 perfect fifth. In this form of just intonation, the highest prime number is. Half an octave, three whole tones, two minor thirds, etc. Web because the basic pitch ratios are 3/2 and 5/4, all pitch ratios are composed of the prime numbers 2, 3 and 5. For instance 100/81 (top left) = 5 x 5 x 2 x 2 / 3 x 3 x 3 x 3. Web making an adjustment to one note for the sake of making both notes match, is called “just intonation”. Web on a piano in just intonation, moving from one tonic to another changes the whole interval makeup of the key, and you get a really specific, visceral feel for where you are on the pitch map. Each musical tone consists of a fundamental resonance and a series of overtones. An adjustment is often made making another major second being 10/9. Employing just intonation, orchestras are. The qualities and relative strengths of the fundamental and of these overtones affect our perception of the pitch itself to some extent and especially our perception of the timbre of the pitch.Just Intonation Chord Chart that is used for wind instruments when
Just intonation Wikipedia
13+ Just Intonation Chart NafisahJimmy
Just intonation (cromatic scale) sheet music for Voice download free in
How to Use Ben Johnston's Just Intonation Notation
7Limit Just Intonation Custom Harmonicas by Andrew Zajac
How to Use Ben Johnston's Just Intonation Notation
Pin by Mike Mashburn on Guitar Chords & Music Theory Just intonation
On "Just" tuning and A = 432 Hz Blog, Item, News and Announcements
How to Use Ben Johnston's Just Intonation Notation
With 84 Pages Of Text And Over 50 Charts And Diagrams, The Just Intonation Primer Explains The Essential Concepts Of Just Intonation In Terms That Practicing Composers And Musicians Will Understand.
Consequently, The Numerator And Denominator Of Each Ratio Are Always A Power Of 2 Or 3.
All Perfect Fifths In The Scale Are In The Ratio 3:2.
Understand The Effects Of Temperature, Dynamics, Reeds, And Mutes On Intonation.
Related Post: